The battery landscape undergoes a transformative evolution with the prominence of Absorbed Glass Mat (AGM) batteries. Known by various monikers such as “dry,” “membrane,” or “starved electrolyte” batteries, AGM batteries have surged in popularity, reshaping the landscape of battery design and resilience.
Table of Contents
What is an AGM Battery?
You might be familiar with the term AGM battery, which stands for Absorbent Glass Mat. But, what exactly does Absorbent Glass Mat (AGM) mean, and how does it contribute to the battery’s superior performance compared to standard lead-acid batteries?
Let’s delve into the fundamentals of sealed lead-acid (SLA) battery construction. All SLA batteries consist of lead plates (positive and negative) and electrolyte, organized into “cells” and housed within a battery case. Some of these batteries are valve-regulated, permitting the release of minor gas amounts that occur during the recombination process during charging. While these batteries allow gas escape, they are spill-proof batteries, often referred to as valve-regulated lead-acid (VRLA), enabling safe operation in almost any position (with the only exception being upside down).
Due to their sealed nature, there is no need to add electrolyte after the manufacturing process, and any generated gases undergo a recombination cycle.
AGM Technology Explained:
In AGM-type batteries, the construction adheres to the same fundamentals as standard SLA, but with the incorporation of a fiberglass mat positioned between each negative and positive plate to absorb the electrolyte. This mat, akin to a sponge, renders the battery non-spillable.
The AGM battery secures the electrolyte in place and operates by permitting the electrolyte to pass through the fiberglass mat. This process optimizes the surface area for the electrolyte to interact with the plates without inundating the battery with excess fluid.
AGM batteries contain just enough electrolyte to keep the mat moist, and in the event of a battery breakage, no free liquid is present to leak out. This design allows for a reduced amount of electrolyte in the battery while maintaining the same energy output as traditional SLA batteries.
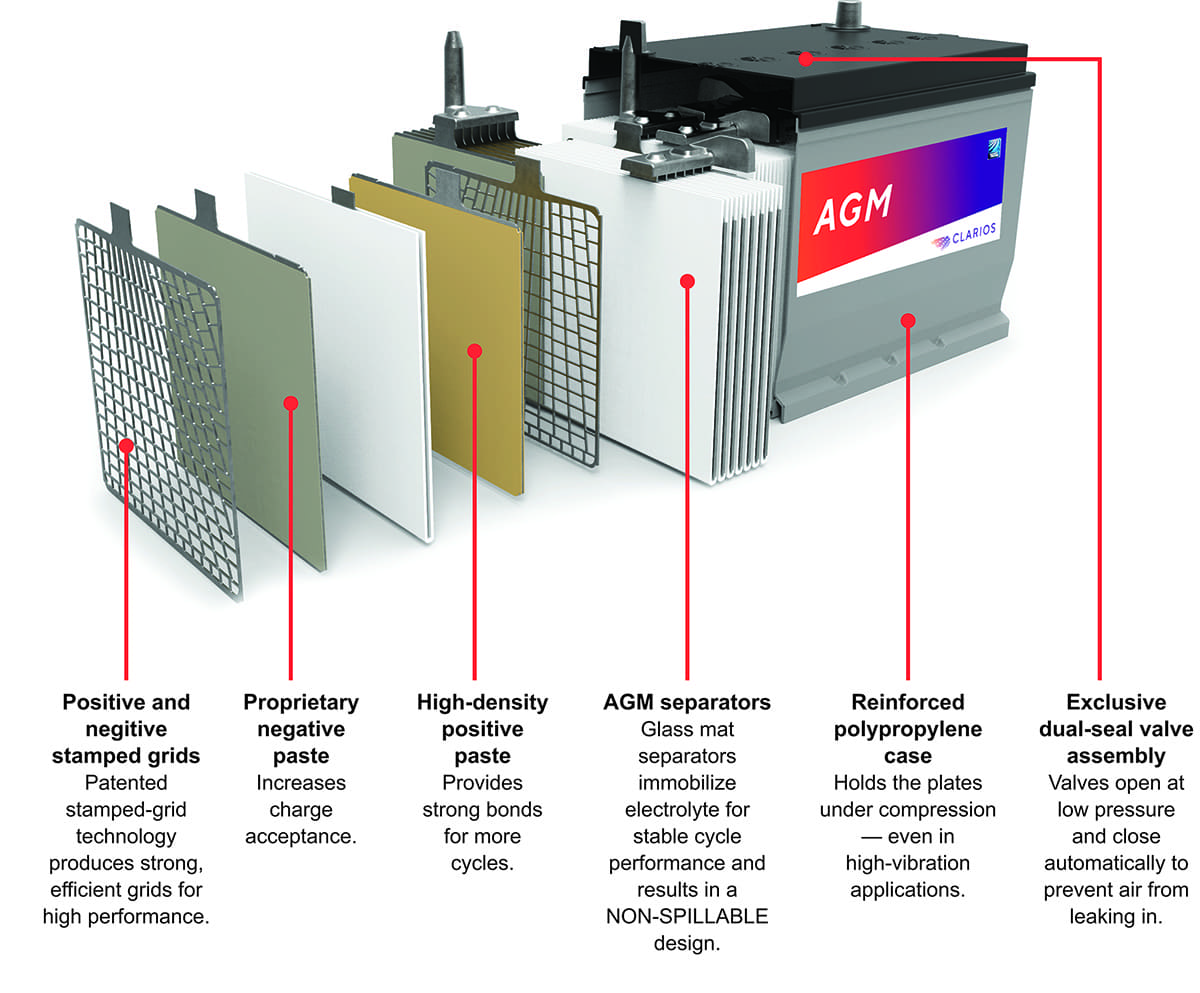
How AGM Batteries Work:
The AGM battery operates with positive and negative lead plates immersed in an electrolyte mixture. An ultra-fine fiberglass mat, sandwiched between the plates, absorbs the electrolyte, ensuring uniform contact with active lead materials.
The design facilitates the flow of electrons in a series circuit through six cells, yielding a total output of 12 volts.
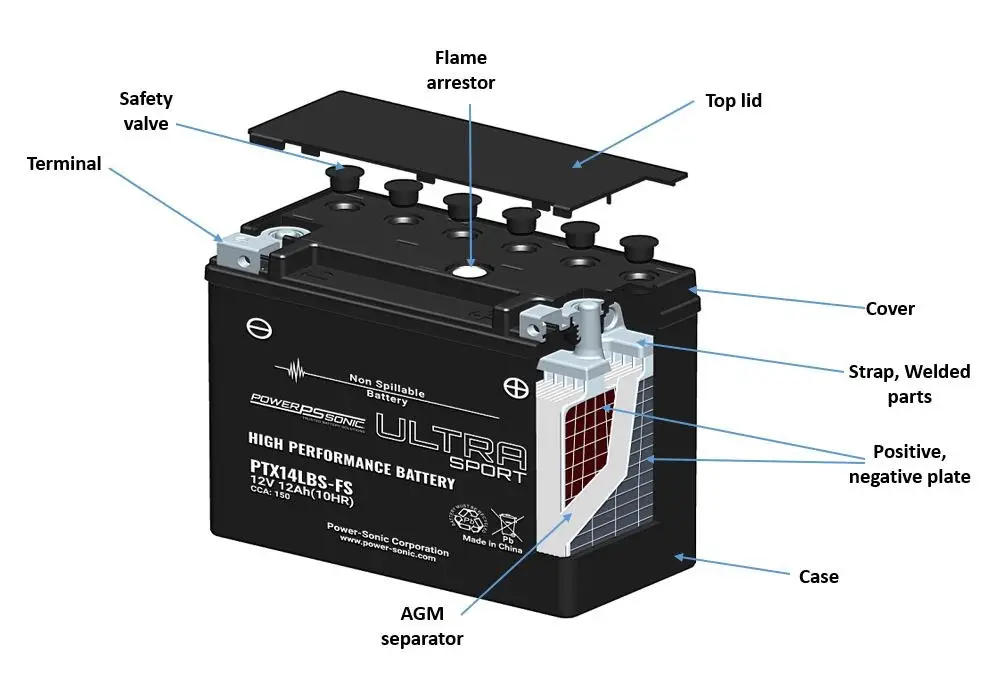
AGM vs. Other Batteries:
AGM batteries stand out in their internal construction, offering advantages such as ease of installation, zero maintenance, and minimal gas formation.
Comparatively, they outshine flooded batteries in terms of lifespan and resistance to extreme temperatures, while also being more cost-effective than gel batteries.
- AGM vs. Gel: AGM batteries surpass gel batteries in lifespan, charging time, and performance in extreme weather conditions.
- AGM vs. Lead-Acid: AGM batteries exhibit better cycling and charging performance, minimal gassing, longer lifespan, and resistance to freezing.
- AGM vs. Lithium: Lithium batteries outshine AGM in weight and lifespan but come at a higher cost, reflecting their superior energy density and deep discharge capability.
- AGM vs. Flooded: AGM batteries excel with a longer lifespan and better performance in extreme temperatures, thanks to their unique design.
Advantages of AGM Batteries:
- Greater mounting flexibility: due to the absorption of acid by glass microfibers.
- Higher voltage output: even in challenging conditions.
- Longer lifespan: attributed to thicker plate design.
- Ideal for start-stop systems: with superior charge acceptance.
- Spill-proof design: ensuring safety and usability.
- Vibration resistance: for enhanced durability.
Disadvantages of AGM Batteries:
- Higher manufacturing cost.
- Sensitivity to overcharging and undercharging.
- Lower specific energy and reduced charging capacity over time.
Uses of AGM Batteries:
AGM batteries find applications in diverse areas, from fuel-efficient vehicles to high-end motorcycles, marine environments, and robotics. Renowned manufacturers like Yuasa and Crown Battery leverage AGM technology for various applications, emphasizing reliability, performance, and adaptability to demanding conditions.
Conclusion:
Despite the initial investment, AGM batteries emerge as a compelling choice for those seeking longer life, faster recharging, and versatility in challenging conditions. As AGM batteries continue to meet the demands of OEM vehicles and gain traction in diverse sectors, their recyclability and eco-friendly nature add an additional layer of appeal to this evolving battery technology.
















 No products in the cart.
No products in the cart.